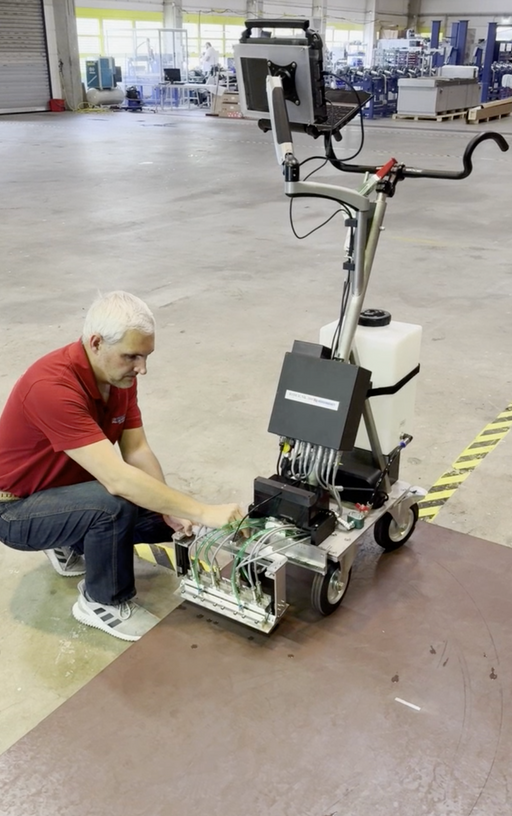
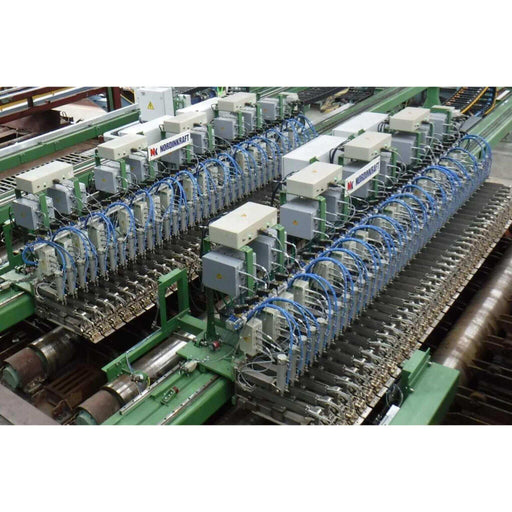
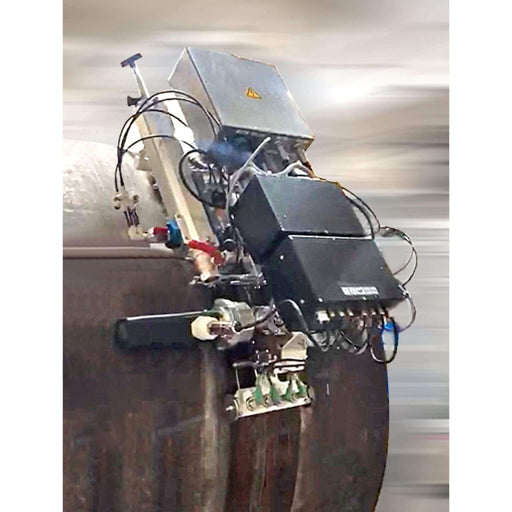
Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is a non-destructive testing (NDT) technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to detect and characterize flaws or discontinuities in materials.
This method works by transmitting a pulse of high-frequency sound waves into the material being tested and then measuring the time taken for the sound waves to reflect back to a receiver. Any changes in the material, such as cracks, voids, or changes in thickness, will cause the sound waves to reflect differently and produce echoes that can be detected and analyzed.
UT can be used to measure the thickness of materials, detect flaws such as cracks or voids, and determine the quality of welds. It is widely used in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and aerospace to ensure the integrity and safety of critical components. It can be performed on a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites, and is a valuable tool for detecting hidden defects that may not be visible to the naked eye. Defects can be detected early and repaired, thus preventing costly failures and ensuring the reliability and safety of critical components.